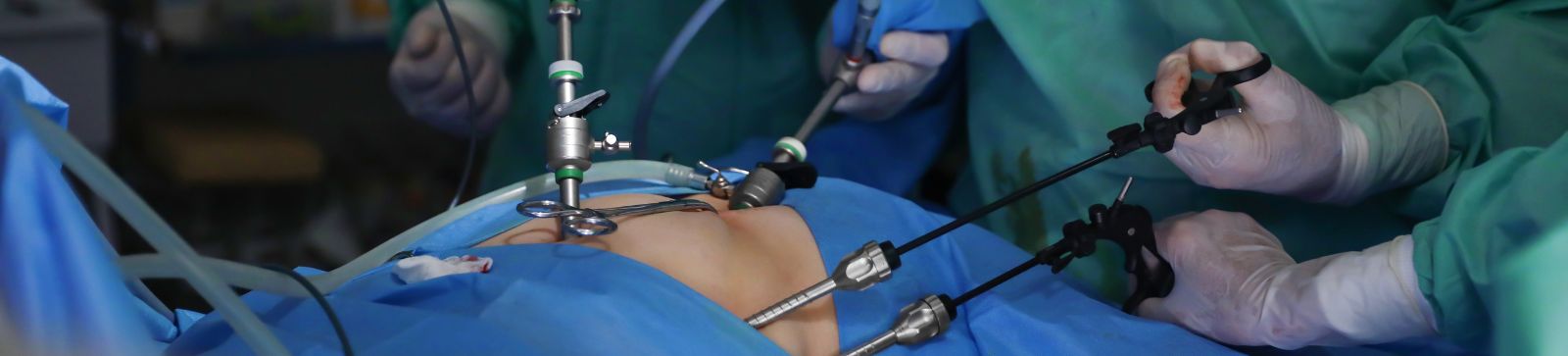
Medical advancements have revolutionized surgery, making procedures safer, quicker, and less painful for patients. One of the most significant innovations is laparoscopy, also known as keyhole surgery. Unlike traditional open surgeries that require large incisions, laparoscopy uses tiny cuts, resulting in faster recovery, minimal scarring, and reduced postoperative pain.
If you or a loved one is considering surgery, understanding laparoscopic techniques can help you make an informed decision. In this blog, we will discuss what laparoscopy is, its benefits, procedures performed using this technique, and what to expect during recovery.
What is Laparoscopy?
A narrowed tube containing a camera (laparoscope) is placed via tiny incision during a laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure. The surgeon may carry out the treatment with extreme precision thanks to this camera's ability to magnify and display the interior organs in real time on a monitor.
Large body incisions are avoided by performing the surgery using long, thin instruments that are placed into additional tiny incisions. Laparoscopy is extremely popular in many medical specialties, including gynecology, urology, gastrointestinal, and general surgery, due to its minimally invasive nature.
Benefits of Keyhole Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy is the preferred method for many treatments because it has several advantages over open surgery. Among the main advantages are:
- Less scarring and smaller incisions: Scarring is low since laparoscopic surgery only necessitates a few tiny incisions rather than a single, big one. This results in less tissue damage and better esthetic results.
- Reduced Pain & Faster Recovery: Patients experience significantly less post-operative pain as compared to open surgeries. Since smaller incisions heal quicker, recovery time is much shorter, allowing patients to return to normal activities sooner.
- Lower Risk of Infection & Bleeding: Smaller incisions mean less blood loss during surgery and a lower risk of infections, making laparoscopy a safer option.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Many laparoscopic procedures are performed as day-care surgeries, meaning patients can go home the same day or within 24 to 48 hours. This reduces hospital costs and helps in faster rehabilitation.
- Better Surgical Precision: The high-definition laparoscopic camera provides clearer and more magnified views than the human eye, enabling greater accuracy and reducing the risk of complications.
Common Laparoscopic Techniques
Numerous medical professions make use of laparoscopy. Typical processes carried out with this method include:
- Gynecological Procedures: Laparoscopic hysterectomy, ovarian cyst removal, and endometriosis treatment.
- Surgical Procedures: Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), appendectomy, and hernia repair.
- Gastrointestinal Surgery: Bariatric (weight loss) surgery, colon surgery for polyps or tumors.
- Urological Surgery: Kidney stone removal, minimally invasive prostate surgery.
Expectations for Laparoscopic Procedures
Before Surgery:
- Pre-operative examinations such as imaging scans, ECGs, and blood tests will be performed by your physician.
- It is recommended that you fast for 6-8 hours prior to the surgery.
During Surgery:
- Several tiny incisions are made in the abdomen.
- A laparoscope (camera) is inserted for visualization.
- The procedure is performed using specialized instruments.
- Surgical glue or dissolvable stitches are used to close the incisions.
After Surgery:
- Patients are observed in a recovery room for a few hours.
- Mild discomfort, bloating, or shoulder pain may occur but usually subsides within a day or two.
- Light movement is encouraged to prevent blood clots.
Recovery After Laparoscopy
Recovery time varies depending on the procedure, but most people heal faster with minimal complications.
- First 24-48 hours: Mild discomfort, bloating, and fatigue. Light activities recommended.
- One week post-surgery: Most daily activities can be resumed, but avoid heavy lifting.
- Full recovery: Typically occurs within 2-4 weeks.
Post-Surgery Care Tips:
- Keep the incision sites clean to avoid infection.
- Take prescribed painkillers as directed.
- Avoid heavy lifting and intense exercise for at least 2-4 weeks.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fiber to prevent constipation.
- Follow up with your surgeon as instructed.
Are There Any Risks?
Although laparoscopic surgery is safe and effective, some rare risks include:
- Bleeding or infection at the incision site.
- Reactions to anesthesia.
- Injury to nearby organs (very rare).
Choosing an experienced laparoscopic surgeon minimizes these risks, ensuring a smooth and successful procedure.
Conclusion
Laparoscopy, or keyhole surgery, has transformed modern surgical procedures, offering patients a safer, less invasive, and more efficient alternative to traditional open surgeries. With benefits such as smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of complications, it has become the preferred choice for many medical treatments.
If you or a loved one is considering surgery, consult your doctor to explore the advantages of laparoscopy for a quicker, less painful healing journey.